pvlib.tracking.singleaxis#
- pvlib.tracking.singleaxis(apparent_zenith, solar_azimuth, axis_slope=0, axis_azimuth=0, max_angle=90, backtrack=True, gcr=0.2857142857142857, cross_axis_slope=0)[source]#
Determine the rotation angle of a single-axis tracker when given particular solar zenith and azimuth angles.
See [1] and [2] for details about the equations. Backtracking may be specified, in which case a ground coverage ratio is required.
Rotation angle is determined in a right-handed coordinate system. The tracker
axis_azimuthdefines the positive y-axis, the positive x-axis is 90 degrees clockwise from the y-axis and parallel to the Earth’s surface, and the positive z-axis is normal to both x and y-axes and oriented skyward. Rotation angletracker_thetais a right-handed rotation around the y-axis in the x, y, z coordinate system and indicates tracker position relative to horizontal. For example, if trackeraxis_azimuthis 180 (oriented south) andaxis_slopeis zero, then atracker_thetaof zero is horizontal, atracker_thetaof 30 degrees is a rotation of 30 degrees towards the west, and atracker_thetaof -90 degrees is a rotation to the vertical plane facing east.- Parameters:
apparent_zenith (float, 1d array, or Series) – Solar apparent zenith angles in decimal degrees.
solar_azimuth (float, 1d array, or Series) – Solar apparent azimuth angles in decimal degrees.
axis_slope (float, default 0) –
The tilt of the axis of rotation (i.e, the y-axis defined by
axis_azimuth) with respect to horizontal.axis_slopemust be >= 0 and <= 90. [degrees]Changed in version 0.14.0: Renamed from
axis_tilttoaxis_slope.axis_azimuth (float, default 0) – The compass direction along which the axis of rotation lies. Measured in decimal degrees east of north. [degrees]
max_angle (float or tuple, default 90) –
A value denoting the maximum rotation angle, in decimal degrees, of the one-axis tracker from its horizontal position (horizontal if axis_slope = 0). If a float is provided, it represents the maximum rotation angle, and the minimum rotation angle is assumed to be the opposite of the maximum angle. If a tuple of (min_angle, max_angle) is provided, it represents both the minimum and maximum rotation angles.
A rotation to
max_angleis a counter-clockwise rotation about the y-axis of the tracker coordinate system. For example, for a tracker withaxis_azimuthoriented to the south, a rotation tomax_angleis towards the west, and a rotation toward-max_angleis in the opposite direction, toward the east. Hence, amax_angleof 180 degrees (equivalent to max_angle = (-180, 180)) allows the tracker to achieve its full rotation capability.backtrack (bool, default True) – Controls whether the tracker has the capability to “backtrack” to avoid row-to-row shading. False denotes no backtrack capability. True denotes backtrack capability.
gcr (float, default 2.0/7.0) – A value denoting the ground coverage ratio of a tracker system that utilizes backtracking; i.e. the ratio between the PV array surface area to the total ground area. A tracker system with modules 2 meters wide, centered on the tracking axis, with 6 meters between the tracking axes has a
gcrof 2/6=0.333. Ifgcris not provided, agcrof 2/7 is default.gcrmust be <=1.cross_axis_slope (float, default 0.0) –
In degrees \(^{\circ}\). See cross_axis_slope.
Changed in version 0.14.0: Renamed from
cross_axis_tilttocross_axis_slope.
- Returns:
dict or DataFrame with the following columns –
tracker_theta: The rotation angle of the tracker is a right-handed rotation defined by axis_azimuth. tracker_theta = 0 is horizontal. [degrees]
aoi: The angle-of-incidence of direct irradiance onto the rotated panel surface. [degrees]
surface_tilt: The angle between the panel surface and the earth surface, accounting for panel rotation. [degrees]
surface_azimuth: The azimuth of the rotated panel, determined by projecting the vector normal to the panel’s surface to the earth’s surface. [degrees]
See also
pvlib.tracking.calc_axis_slope,pvlib.tracking.calc_cross_axis_slope,pvlib.tracking.calc_surface_orientationReferences
Examples using pvlib.tracking.singleaxis#
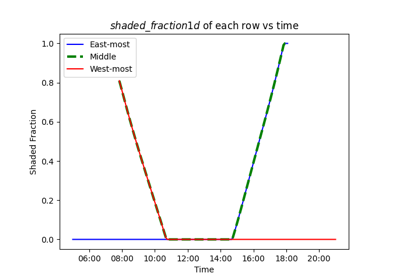
Shaded fraction of a horizontal single-axis tracker
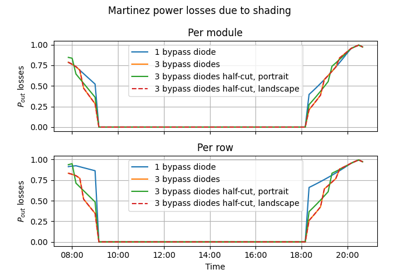
Modelling shading losses in modules with bypass diodes